The Urinary Tract Infection Cause, Symptoms and Test
The Urinary Tract Infection Cause, Symptoms and Test
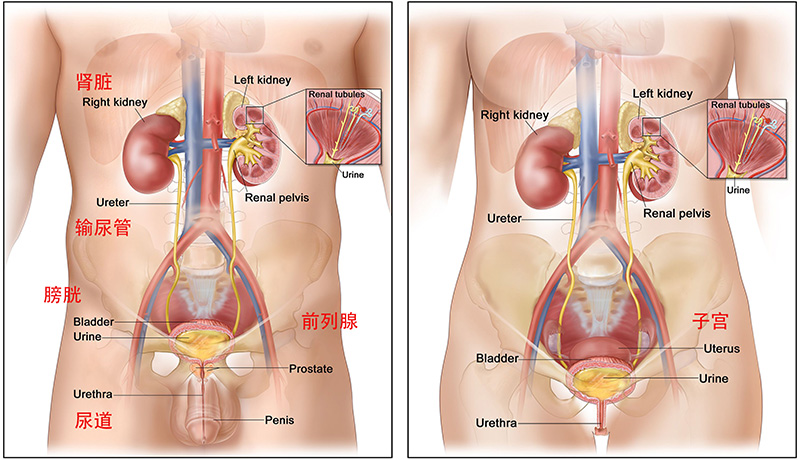
A condition in which bacteria invade and grow in the urinary tract (the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra). Most urinary tract infections occur in the bladder or urethra. Signs and symptoms may include pain or burning during urination, cloudy or bad-smelling urine, blood in the urine, feeling a need to urinate often or right away, pain in the back or lower abdomen, fever, chills, and fatigue. Certain conditions, such as diabetes, hormone changes, kidney stones, an enlarged prostate, or a spinal cord injury, may increase the risk of a urinary tract infection. Other risk factors include radiation therapy or surgery to the pelvis, taking certain types of medicines (such as anticancer drugs), or using a catheter to empty the bladder. Urinary tract infections are common, especially in women. Also called UTI.
The infection can occur at different points in the urinary tract, including the:
- Bladder — An infection in the bladder is also called cystitisor a bladder infection.
- Kidneys — An infection of one or both kidneys is called pyelonephritisor a kidney infection.
- Ureters — The tubes that take urine from each kidney to the bladder are rarely the only site of infection.
- Urethra — An infection of the tube that empties urine from the bladder to the outside is called urethritis.
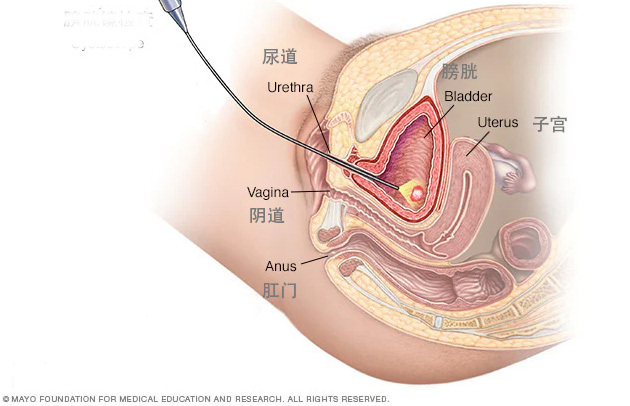
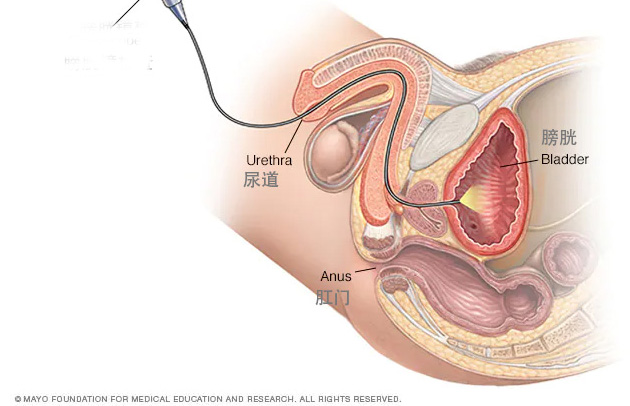
causes
Most UTIs are caused by bacteria that enter the urethra and then the bladder. The infection most commonly develops in the bladder, but can spread to the kidneys. Most of the time, your body can get rid of these bacteria. However, certain conditions increase the risk for having UTIs.
Women tend to get them more often because their urethra is shorter and closer to the anus than in men. Because of this, women are more likely to get an infection after sexual activity or when using a diaphragm for birth control. Menopause also increases the risk for a UTI.
The following also increase your chances of developing a UTI:
- Diabetes
- Advanced age
- Conditions that affect personal care habits (such as Alzheimer diseaseand delirium)
- Problems emptying the bladder completely
- Having a urinary catheter
- Bowel incontinence
- Enlarged prostate, narrowed urethra, or anything that blocks the flow of urine
- Kidney stones
- Staying still (immobile) for a long period of time (for example, while you are recovering from a hip fracture)
- Pregnancy
- Surgery or other procedure involving the urinary tract
Symptoms
The symptoms of a bladder infection include:
- Cloudyor bloody urine, which may have a foul or strong odor
- Low grade fever in some people
- Pain or burning with urination
- Pressure or cramping in the lower abdomen or back
- Strong need to urinate often, even right after the bladder has been emptied
If the infection spreads to your kidneys, symptoms may include:
- Chillsand shaking or night sweats
- Fatigueand a general ill feeling
- Fever above 101°F (38.3°C)
- Pain in the side, back, or groin
- Flushed, warm, or reddened skin
- Mental changes or confusion(in older people, these symptoms often are the only signs of a UTI)
- Nauseaand vomiting
- Severe abdominal pain (sometimes)
Exams and Tests
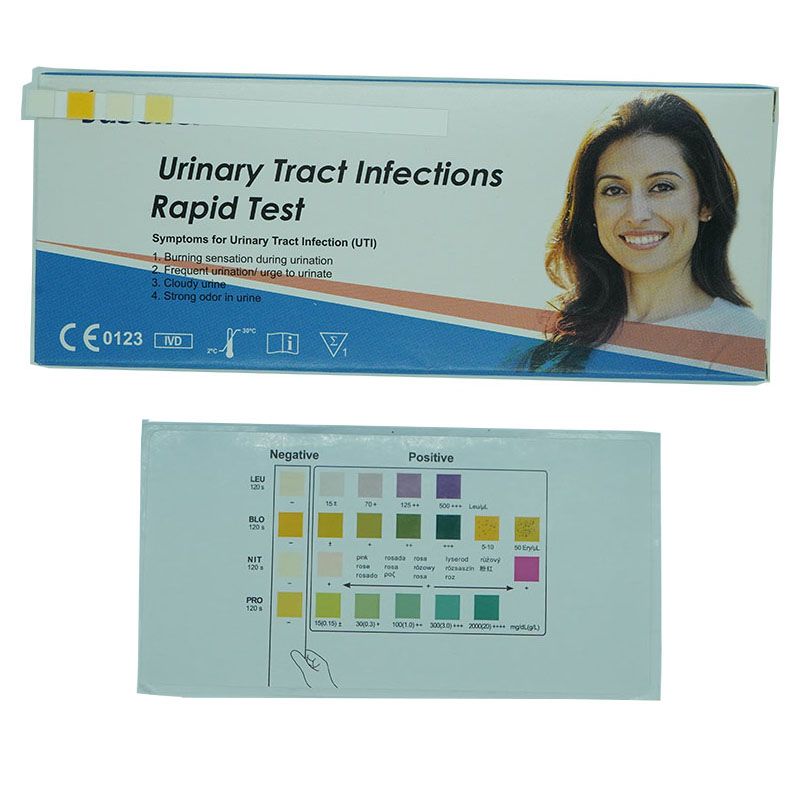
Most of the time, you will need to provide a urine sample for the following tests:
UTI(Urinary Tract Infection) Test — The test is for the qualitative detection of the following analytes in urine: Leukocytes, Blood, Nitrite and Protein. The Urinary Tract Infections Test (Urine) is for single use in self-testing..
Treatment
Your health care provider must first decide if the infection is just in the bladder, or if it has spread to the kidneys and how severe it is.
